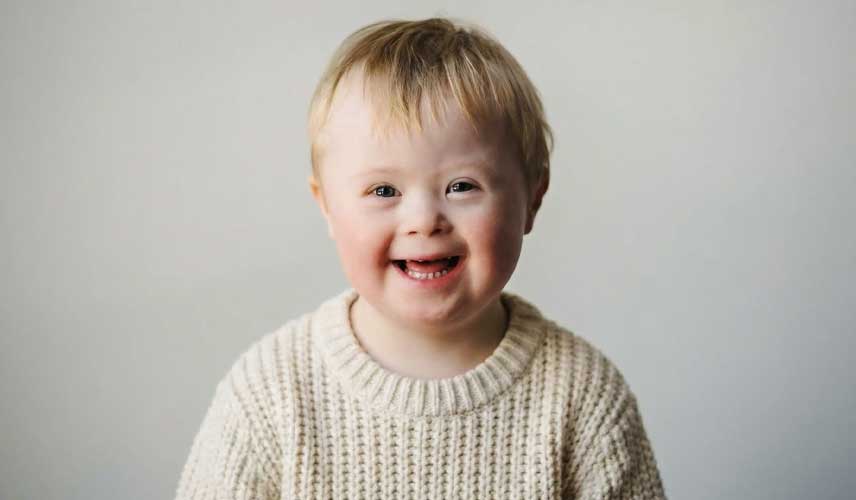

Down Syndrome Diagnosis Methods

Down syndrome, also known as a type of chromosomal disorder, is one of the most common causes of intellectual disability. This disorder affects the individual's development throughout their life and can impact babies of mothers of all ages, but the likelihood is higher in babies of older mothers. The most common cause of the syndrome is the presence of three copies of the 21st chromosome instead of the usual two. For this reason, it is also referred to as trisomy 21. The methods for diagnosing Down syndrome are divided into two groups: screening tests and diagnostic tests. Screening tests are only probability-based tests, while definitive diagnoses are made through diagnostic tests.
Down Syndrome Screening Tests
Tests Conducted in the First 3 Months
These tests, which are based on the levels of two proteins in the mother's blood and certain characteristics of the fetus identified via ultrasound, are performed between the 11th and 14th weeks of pregnancy.
Tests Conducted in the Second 3 Months
Tests that calculate the likelihood of the baby having Down syndrome based on the levels of three proteins in the mother's blood are called the triple screening test, while those that consider the levels of four proteins are referred to as the quadruple screening test. These tests are conducted between the 16th and 18th weeks of pregnancy.
Cell-Free DNA Tests
These tests, which examine DNA fragments belonging to the baby in the mother's blood, have a higher accuracy rate than the aforementioned tests.
Down Syndrome Diagnostic Tests
Chorionic Villus Sampling
Chorionic villus sampling is a procedure performed between the 9th and 14th weeks of pregnancy. It involves taking a sample from the placenta, which nourishes the baby, by inserting a thin needle through a suitable area of the pregnant woman's abdomen or through the cervix.
Amniocentesis
This involves taking a sample of the amniotic fluid in which the baby floats. The cells in the fluid are examined to determine the chromosomal structure. It may seem frightening as it can lead to miscarriage, but when performed by an experienced doctor, the risk is quite low. Generally, it is performed between the 15th and 20th weeks of pregnancy, but it can also be done at different times depending on the purpose. Performing it before the 15th week of pregnancy increases the risk of miscarriage.
Cordocentesis
This is a diagnostic test performed between the 18th and 22nd weeks of pregnancy. It is conducted by taking blood from the umbilical cord. It is also used when there is a need to administer blood or medication to the baby. It provides information about blood type, blood disorders, and factors that may lead to developmental delays.
Postnatal Diagnosis
Down syndrome diagnosis can also be made after birth. A baby with Down syndrome can be easily recognized due to its typical features. The head is smaller than normal and flat at the back, the palate is narrow and short, and the mouth is small, which may cause the tongue to protrude. The face is flat, and the bridge of the nose is particularly flattened.
About 70% to 80% of babies with Down syndrome have a simian line in their palms, which is a single line that runs across the palm. This is a condition that is rarely seen in the normal population. Additionally, their muscle and joint structure is weak.
Child Health and Safety Other Content in the Category

Child Health and Safety
Newborn Care

Child Health and Safety
My Baby Refuses to Eat Solid Food

Child Health and Safety
Ways to Protect Children from the Coronavirus

Child Health and Safety
What to Do to Instill Brushing Habits in Children

Child Health and Safety
Child Safety: Medications Should Be Stored Out of Reach of Children

Child Health and Safety
10 Effective Tips for Child Health

Child Health and Safety
8 Factors That Cause Babies to Cry

Child Health and Safety
Down Syndrome Diagnosis Methods

Child Health and Safety
When Do Babies Crawl
Child Health and Safety
Information About Teething Period in Babies

Child Health and Safety
How Much Water Should Babies Drink?

Child Health and Safety
10 Things to Do for a Healthy Pregnancy

Child Health and Safety
10 Ways to Prevent Sugar Consumption in Children

Child Health and Safety
Frequently Asked Questions About Cancer and Chemotherapy

Child Health and Safety
