
Iron Deficiency Anemia in Children

Anemia refers to a decrease in the functional capacity of the blood to carry oxygen from the lungs, resulting in a lack of oxygen in the tissues. A lack of oxygen in the tissues means that the entire body is affected, which is particularly a significant issue for those in the developmental stage. Iron deficiency anemia is a condition where the amount of iron in the body falls below normal levels for various reasons. In iron deficiency, anemia occurs because the iron stores are insufficient for blood production. It is the most common blood disorder seen in infancy and childhood. Incidence in infants and children aged 0-24 months: Iron deficiency is considered the most common cause of anemia in infants and children, especially between the ages of 6-24 months.
The iron level is high in the first months after the baby's birth. It begins to decrease in the following months. Iron is widely used in the human body. Its deficiency affects all systems and clinical findings emerge. Causes In our country, iron deficiency anemia in children is most commonly seen due to inadequate nutrition, low socio-economic status, inflammation, and diseases caused by parasites. Diagnosis After taking the patient’s history, laboratory tests are performed. In the complete blood count, values below the age-appropriate Hb levels in children are considered anemia. Additionally, the diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia can be made by measuring the levels of serum iron and ferritin, which indicates iron stores.
What are the prevention and treatment methods? There are five key practices important in preventing iron deficiency anemia. These include determining the prevalence of anemia, providing nutritional education, administering iron supplements, controlling viral, bacterial, and parasitic diseases, and fortifying foods with iron.
To prevent anemia, the globally accepted prophylactic iron supplementation is the most important protective method. Iron supplementation given to infants should continue for 8 months. A study conducted on 6-month-old infants showed that the incidence of iron deficiency anemia decreased from 30% to 2% with prophylactic iron supplementation. The same study found that children receiving prophylactic iron supplementation had improved mental and physical scores by the 13th month.
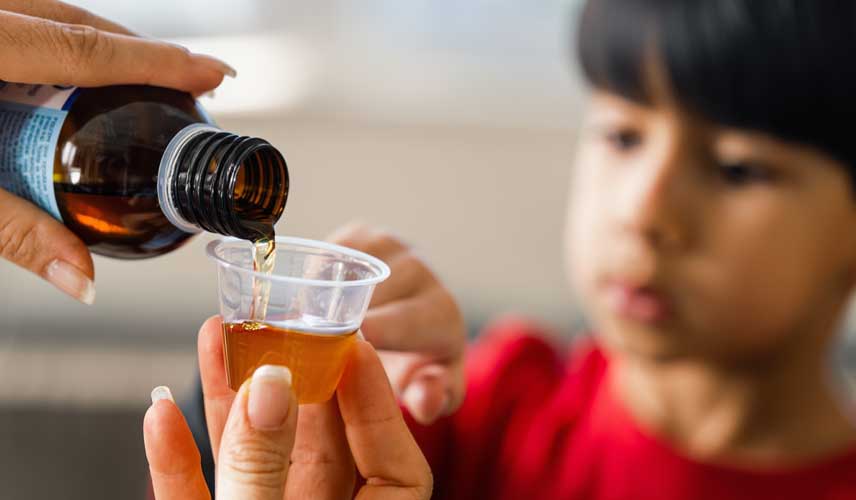
It has been observed that those fed with formula and cow's milk instead of breast milk in the first 6 months have a higher occurrence of iron deficiency anemia. Breast milk is sufficient for infants' nutrition in the first 6 months after birth. After that, it is recommended to introduce additional foods rich in iron alongside breast milk. In the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in children, the medication is better tolerated when given as a single dose half an hour before the morning meal for children and infants under 24 months.
The iron medication used in treatment is administered orally. The patient's values return to normal after 2-4 weeks. However, treatment should continue for a few months to replenish iron stores. Iron medication can change the color of teeth and stool. It can be given through a straw or diluted. It is not recommended to consume it with dairy products. For patients experiencing absorption issues in the intestines, iron is injected into the buttock with a needle.
Child Health and Safety Other Content in the Category

Child Health and Safety
Newborn Care

Child Health and Safety
My Baby Refuses to Eat Solid Food

Child Health and Safety
Ways to Protect Children from the Coronavirus

Child Health and Safety
What to Do to Instill Brushing Habits in Children

Child Health and Safety
Child Safety: Medications Should Be Stored Out of Reach of Children

Child Health and Safety
10 Effective Tips for Child Health

Child Health and Safety
8 Factors That Cause Babies to Cry

Child Health and Safety
Down Syndrome Diagnosis Methods

Child Health and Safety
When Do Babies Crawl
Child Health and Safety
Information About Teething Period in Babies

Child Health and Safety
How Much Water Should Babies Drink?

Child Health and Safety
10 Things to Do for a Healthy Pregnancy

Child Health and Safety
10 Ways to Prevent Sugar Consumption in Children

Child Health and Safety
Frequently Asked Questions About Cancer and Chemotherapy

Child Health and Safety
